which disaccharide has no free aldehyde or ketone group Disaccharide aldehyde linkage hydrolyzes mechanism catalyst write group transcribed text show alpha explain
Hey there! Did you know that carbohydrates play a crucial role in our body’s energy production? Well, let’s dive into the fascinating world of disaccharides and explore one in particular - sucrose.
Sucrose: The Sweetest of All Disaccharides

What is a Reducing Sugar?
To understand why sucrose is not considered a reducing sugar, we first need to understand what reducing sugars are. Reducing sugars are carbohydrates that have the ability to reduce other substances, specifically, metallic ions. This reduction reaction results in the formation of a compound called a “reducing end.”
This reduction ability is due to the presence of certain functional groups in the sugar molecule. One such functional group is the aldehyde group, which has a free carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of the molecule. In simpler terms, reducing sugars have the potential to donate electrons, thereby reducing other substances.
Sucrose’s Missing Aldehyde Group
Now, let’s get back to sucrose. Take a look at the chemical structure of sucrose - it consists of two monosaccharides, glucose, and fructose. But here’s the catch - neither glucose nor fructose has a free aldehyde group! In sucrose, the aldehyde group of glucose and the ketone group of fructose reacted, resulting in the formation of a glycosidic bond.
As a result, sucrose lacks the essential functional group necessary for the reducing ability. Without the free carbonyl group, sucrose cannot donate electrons and thus does not exhibit reducing sugar properties.
Importance of Sucrose
Just because sucrose is not classified as a reducing sugar doesn’t mean it isn’t important! On the contrary, sucrose is a significant source of energy for our bodies. When we consume sucrose, it gets broken down into glucose and fructose through the action of digestive enzymes.
Once broken down, glucose and fructose can be used by our cells for immediate energy production. Additionally, excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for later use. So, next time you enjoy a spoonful of sugar in your tea or indulge in your favorite dessert, you now know that sucrose plays a vital role in keeping you energized!
In conclusion, sucrose may not be classified as a reducing sugar due to the absence of a free aldehyde group, but its role in providing energy cannot be understated. Understanding the chemistry behind disaccharides like sucrose helps us appreciate the intricate processes that occur within our body. So, the next time you take a sip of that sweet beverage or bite into a sugary treat, remember the fascinating world of carbohydrates that makes it all possible!
If you are searching about Disaccharides you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Disaccharides like Solved Question 13 (2 points) Which disaccharide has a free | Chegg.com, Is a sucrose a ‘reducing sugar’ and if not, why not? - Quora and also Solved What disaccharide(s) has (have) a free aldehyde | Chegg.com. Here you go:
Disaccharides
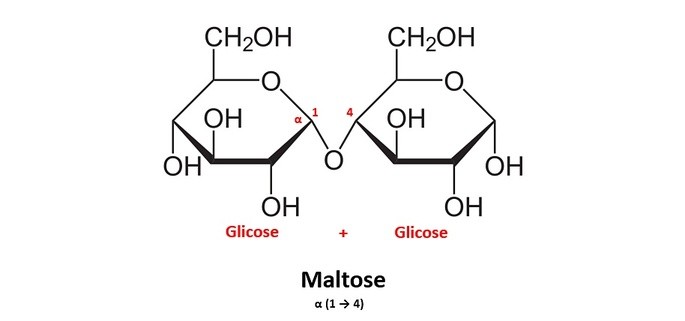 allthematters.comdisaccharides
allthematters.comdisaccharides
Disaccharides - Definition, Function, Structure & Examples
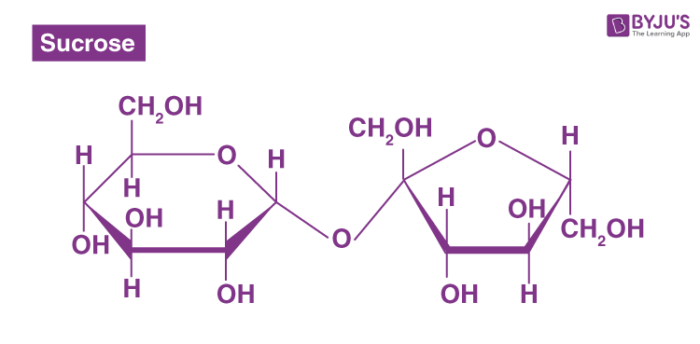 byjus.comdisaccharides examples maltose sucrose
byjus.comdisaccharides examples maltose sucrose
Is A Sucrose A ‘reducing Sugar’ And If Not, Why Not? - Quora
 www.quora.comSolved Question 13 (2 Points) Which Disaccharide Has A Free | Chegg.com
www.quora.comSolved Question 13 (2 Points) Which Disaccharide Has A Free | Chegg.com
 www.chegg.comdisaccharide points
www.chegg.comdisaccharide points
Solved What Disaccharide(s) Has (have) A Free Aldehyde | Chegg.com

Disaccharides examples maltose sucrose. Solved question 13 (2 points) which disaccharide has a free. Disaccharide points